Build a Secure Node.js App with SQL Server
I am a long-time relational database nerd, specifically SQL Server. At times in my career, I’ve focused on database design, deployments, migrations, administration, query optimization, and carefully crafting stored procedures, triggers, and views.
I’ve written applications on top of SQL Server using Visual Basic, “Classic” ASP, ASP.NET, and, in recent years, Node.js. Yes, it’s true. You can build Node.js applications with SQL Server!
In this tutorial, you will learn the basics of creating a Node.js web application using SQL Server by creating a simple calendar application.
Note: In May 2025, the Okta Integrator Free Plan replaced Okta Developer Edition Accounts, and the Okta CLI was deprecated.
We preserved this post for reference, but the instructions no longer work exactly as written. Replace the Okta CLI commands by manually configuring Okta following the instructions in our Developer Documentation.
Set Up Your Node.js Development Environment
Before you get started, you’ll need a couple of things:
- Node.js version 8.0 or higher
- Access to SQL Server version 2012 or higher
If you don’t already have an instance of SQL Server you can connect to, you can install one locally for development and testing.
Install SQL Server on Windows
Download and install SQL Server Developer Edition.
Install SQL Server on Mac or Linux
- Install Docker.
- Run the following in a terminal. This will download the latest version of SQL Server 2017 for Linux and create a new container named
sqlserver.
docker pull microsoft/mssql-server-linux:2017-latest
docker run -d --name sqlserver -e 'ACCEPT_EULA=Y' -e 'SA_PASSWORD=P@55w0rd' -e 'MSSQL_PID=Developer' -p 1433:1433 microsoft/mssql-server-linux:2017-latest
Note: For more information on running SQL Server for Linux, see SQL Server Running on a Mac?!
Set Up the SQL Database
You will need a SQL database to for this tutorial. If you are running SQL Server locally and don’t already have a database, you can create one with the following script.
Note: If you have Visual Studio Code, you can use the excellent mssql extension to run SQL scripts. Or, you can use an application like Azure Data Studio.
USE master;
GO
CREATE DATABASE calendar; -- change this to whatever database name you desire
GO
Next, create a new table named events. This is the table you will use to store calendar events.
-- Dropping events table...
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS events;
-- Create events table...
CREATE TABLE events (
id int IDENTITY(1, 1) PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED NOT NULL
, userId nvarchar(50) NOT NULL
, title nvarchar(200) NOT NULL
, description nvarchar(1000) NULL
, startDate date NOT NULL
, startTime time(0) NULL
, endDate date NULL
, endTime time(0) NULL
, INDEX idx_events_userId ( userId )
);
Create a Node.js Web Application
With Node.js you can choose from lots of great frameworks for creating web applications. In this tutorial, you will use hapi, my personal favorite. Originally created by Walmart engineers, it is suitable for building APIs, services, and complete web applications.
Open up a command prompt (Windows) or a terminal (Mac or Linux), and change the current directory to where you want to create your project. Create a folder for your project, and change to the new folder.
mkdir node-sql-tutorial
cd node-sql-tutorial
A package.json file is required for Node.js projects and includes things like project information, scripts, and dependencies. Use the npm command to create a package.json file in the project folder.
npm init -y
Next, install hapi as a dependency.
npm install hapi@18
Now open the project in your editor of choice.
If you don’t already have a favorite code editor, I recommend installing Visual Studio Code. VS Code has exceptional support for JavaScript and Node.js, such as smart code completion and debugging. There’s also a vast library of free extensions contributed by the community.
Node.js Project Structure
Most “hello world” examples of Node.js applications start with everything in a single JavaScript file. However, it’s essential to set up a good project structure to support your application as it grows.
There are countless opinions on how you might organize a Node.js project. In this tutorial, the final project structure will be similar to the following.
├── package.json
├── client
├── src
│ ├── data
│ ├── plugins
│ ├── routes
│ └── views
└── test
Create a Basic Server with Routes
Create a folder named src. In this folder, add a new file named index.js. Open the file and add the following JavaScript.
"use strict";
const server = require( "./server" );
const startServer = async () => {
try {
// todo: move configuration to separate config
const config = {
host: "localhost",
port: 8080
};
// create an instance of the server application
const app = await server( config );
// start the web server
await app.start();
console.log( `Server running at http://${ config.host }:${ config.port }...` );
} catch ( err ) {
console.log( "startup error:", err );
}
};
startServer();
Create a new file under src named server.js. Open the file and add the following.
"use strict";
const Hapi = require( "hapi" );
const routes = require( "./routes" );
const app = async config => {
const { host, port } = config;
// create an instance of hapi
const server = Hapi.server( { host, port } );
// store the config for later use
server.app.config = config;
// register routes
await routes.register( server );
return server;
};
module.exports = app;
One of the reasons for separating server configuration from application startup is it will be easier to test the application.
Next, create a folder under src named routes. In this folder, add a new file named index.js. Open the file and add the following.
"use strict";
module.exports.register = async server => {
server.route( {
method: "GET",
path: "/",
handler: async ( request, h ) => {
return "My first hapi server!";
}
} );
};
Finally, edit the package.json file and change the "main" property value to "src/index.js". This property instructs Node.js on which file to execute when the application starts.
"main": "src/index.js",
Now you can start the application. Go back to your command/terminal window and type in the following command.
node .
You should see the message Server running at http://localhost:8080.... Open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080. Your browser should display something like the following.
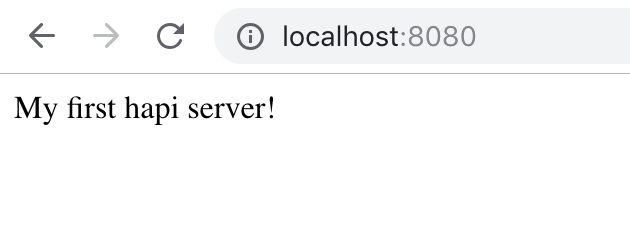
Success!
Note: To stop the Node.js application, go to the command/terminal window and press
CTRL+C.
Manage Your Node.js Application Configuration
Before we get into writing code to interact with SQL Server, we need a good way to manage our application’s configuration, such as our SQL Server connection information.
Node.js applications typically use environment variables for configuration. However, managing environment variables can be a pain. dotenv is a popular Node.js package that exposes a .env configuration file to Node.js as if it were all set using environment variables.
First, install dotenv as a project dependency.
npm install dotenv@6
Create a file named .env in the root folder of the project, and add the following configuration.
# Set NODE_ENV=production when deploying to production
NODE_ENV=development
# hapi server configuration
PORT=8080
HOST=localhost
HOST_URL=http://localhost:8080
COOKIE_ENCRYPT_PWD=superAwesomePasswordStringThatIsAtLeast32CharactersLong!
# SQL Server connection
SQL_USER=dbuser
SQL_PASSWORD=P@55w0rd
SQL_DATABASE=calendar
SQL_SERVER=servername
# Set SQL_ENCRYPT=true if using Azure
SQL_ENCRYPT=false
# Okta configuration
OKTA_ORG_URL=https://{yourOktaDomain}
OKTA_CLIENT_ID={yourClientId}
OKTA_CLIENT_SECRET={yourClientSecret}
Update the SQL Server configuration with your database configuration information. We will cover some of the other settings later.
Note: When using a source control system such as git, do not add the
.envfile to source control. Each environment requires a custom.envfile and may contain secrets that should not be stored in a repository. It is recommended you document the values expected in the project README and in a separate.env.samplefile.
Next, create a file under src named config.js and add the following code.
"use strict";
const assert = require( "assert" );
const dotenv = require( "dotenv" );
// read in the .env file
dotenv.config();
// capture the environment variables the application needs
const { PORT,
HOST,
HOST_URL,
COOKIE_ENCRYPT_PWD,
SQL_SERVER,
SQL_DATABASE,
SQL_USER,
SQL_PASSWORD,
OKTA_ORG_URL,
OKTA_CLIENT_ID,
OKTA_CLIENT_SECRET
} = process.env;
const sqlEncrypt = process.env.SQL_ENCRYPT === "true";
// validate the required configuration information
assert( PORT, "PORT configuration is required." );
assert( HOST, "HOST configuration is required." );
assert( HOST_URL, "HOST_URL configuration is required." );
assert( COOKIE_ENCRYPT_PWD, "COOKIE_ENCRYPT_PWD configuration is required." );
assert( SQL_SERVER, "SQL_SERVER configuration is required." );
assert( SQL_DATABASE, "SQL_DATABASE configuration is required." );
assert( SQL_USER, "SQL_USER configuration is required." );
assert( SQL_PASSWORD, "SQL_PASSWORD configuration is required." );
assert( OKTA_ORG_URL, "OKTA_ORG_URL configuration is required." );
assert( OKTA_CLIENT_ID, "OKTA_CLIENT_ID configuration is required." );
assert( OKTA_CLIENT_SECRET, "OKTA_CLIENT_SECRET configuration is required." );
// export the configuration information
module.exports = {
port: PORT,
host: HOST,
url: HOST_URL,
cookiePwd: COOKIE_ENCRYPT_PWD,
sql: {
server: SQL_SERVER,
database: SQL_DATABASE,
user: SQL_USER,
password: SQL_PASSWORD,
options: {
encrypt: sqlEncrypt
}
},
okta: {
url: OKTA_ORG_URL,
clientId: OKTA_CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: OKTA_CLIENT_SECRET
}
};
Update src/index.js to use the new config module you just created.
"use strict";
const config = require( "./config" );
const server = require( "./server" );
const startServer = async () => {
try {
// create an instance of the server application
const app = await server( config );
// start the web server
await app.start();
console.log( `Server running at http://${ config.host }:${ config.port }...` );
} catch ( err ) {
console.log( "startup error:", err );
}
};
startServer();
Create a Node.js API With SQL Server
Now we can get to the fun part! In this step, you are going to add a route to hapi to query the database for a list of events and return them as JSON. You are going to create a SQL Server client plugin for hapi, and organize the data access layer in a way that will make it easy to add new APIs in the future.
First, you need to install a few dependencies, the most important being the mssql package.
npm install mssql@4 fs-extra@7
Create the SQL Data Access Layer
Using SQL Server with Node.js and the mssql package usually follows these steps:
- Create an instance of the
mssqlpackage. - Create a SQL connection with
connect(). - Use the connection to create a new SQL
request. - Set any input parameters on the request.
- Execute the request.
- Process the results (e.g. recordset) returned by the request.
Creating connections to SQL Server is a relatively expensive operation. There is also a practical limit to the number of connections that can be established. By default, the mssql package’s .connect() function creates and returns a connection “pool” object. A connection pool increases the performance and scalability of an application.
When a query request is created, the SQL client uses the next available connection in the pool. After the query is executed, the connection is returned to the connection to the pool.
Create a folder under src named data. Create a new file under src/data named index.js. Add the following code to this file.
"use strict";
const events = require( "./events" );
const sql = require( "mssql" );
const client = async ( server, config ) => {
let pool = null;
const closePool = async () => {
try {
// try to close the connection pool
await pool.close();
// set the pool to null to ensure
// a new one will be created by getConnection()
pool = null;
} catch ( err ) {
// error closing the connection (could already be closed)
// set the pool to null to ensure
// a new one will be created by getConnection()
pool = null;
server.log( [ "error", "data" ], "closePool error" );
server.log( [ "error", "data" ], err );
}
};
const getConnection = async () => {
try {
if ( pool ) {
// has the connection pool already been created?
// if so, return the existing pool
return pool;
}
// create a new connection pool
pool = await sql.connect( config );
// catch any connection errors and close the pool
pool.on( "error", async err => {
server.log( [ "error", "data" ], "connection pool error" );
server.log( [ "error", "data" ], err );
await closePool();
} );
return pool;
} catch ( err ) {
// error connecting to SQL Server
server.log( [ "error", "data" ], "error connecting to sql server" );
server.log( [ "error", "data" ], err );
pool = null;
}
};
// this is the API the client exposes to the rest
// of the application
return {
events: await events.register( { sql, getConnection } )
};
};
module.exports = client;
When using SQL Server with Node.js, one of the most critical things to get right is properly handling connection errors when they occur. Internally, the sql/data module has two important functions: getConnection and closePool. getConnection returns the active connection pool or creates one if necessary. When any connection error occurs, closePool makes sure the previously active pool is disposed to prevent the module from reusing it.
Create a new file under src/data named utils.js. Add the following code to this file.
"use strict";
const fse = require( "fs-extra" );
const { join } = require( "path" );
const loadSqlQueries = async folderName => {
// determine the file path for the folder
const filePath = join( process.cwd(), "src", "data", folderName );
// get a list of all the files in the folder
const files = await fse.readdir( filePath );
// only files that have the .sql extension
const sqlFiles = files.filter( f => f.endsWith( ".sql" ) );
// loop over the files and read in their contents
const queries = {};
for ( let i = 0; i < sqlFiles.length; i++ ) {
const query = fse.readFileSync( join( filePath, sqlFiles[ i ] ), { encoding: "UTF-8" } );
queries[ sqlFiles[ i ].replace( ".sql", "" ) ] = query;
}
return queries;
};
module.exports = {
loadSqlQueries
};
Although it’s possible to embed SQL queries as strings in JavaScript code, I believe it’s better to keep the queries in separate .sql files and load them at startup. This utils module loads all the .sql files in a given folder and returns them as a single object.
Create a new folder under src/data named events. Add a new file under src/data/events named index.js. Add the following code to this file.
"use strict";
const utils = require( "../utils" );
const register = async ( { sql, getConnection } ) => {
// read in all the .sql files for this folder
const sqlQueries = await utils.loadSqlQueries( "events" );
const getEvents = async userId => {
// get a connection to SQL Server
const cnx = await getConnection();
// create a new request
const request = await cnx.request();
// configure sql query parameters
request.input( "userId", sql.VarChar( 50 ), userId );
// return the executed query
return request.query( sqlQueries.getEvents );
};
return {
getEvents
};
};
module.exports = { register };
Add a new file under src/data/events named getEvents.sql. Add the following SQL to this file.
SELECT [id]
, [title]
, [description]
, [startDate]
, [startTime]
, [endDate]
, [endTime]
FROM [dbo].[events]
WHERE [userId] = @userId
ORDER BY
[startDate], [startTime];
Notice in the last two files you are using a parameterized query, passing @userId as a named parameter, which guards against SQL injection attacks.
Create a Database Client Plugin
Next, you will add a database client plugin to make it easy to run SQL queries from other parts of the application, such as when a user requests an API. In other frameworks, this concept might be known as middleware, but hapi uses the term plugin.
Create a new folder under src named plugins. Create a new file under src/plugins named index.js. Add the following code.
"use strict";
const sql = require( "./sql" );
module.exports.register = async server => {
// register plugins
await server.register( sql );
};
Create a new file under src/plugins named sql.js. Add the following code.
"use strict";
// import the data access layer
const dataClient = require( "../data" );
module.exports = {
name: "sql",
version: "1.0.0",
register: async server => {
// get the sql connection information
const config = server.app.config.sql;
// create an instance of the database client
const client = await dataClient( server, config );
// "expose" the client so it is available everywhere "server" is available
server.expose( "client", client );
}
};
Next, update src/server.js to register plugins.
"use strict";
const Hapi = require( "hapi" );
const plugins = require( "./plugins" );
const routes = require( "./routes" );
const app = async config => {
const { host, port } = config;
// create an instance of hapi
const server = Hapi.server( { host, port } );
// store the config for later use
server.app.config = config;
// register plugins
await plugins.register( server );
// register routes
await routes.register( server );
return server;
};
module.exports = app;
Add an API Route
Now you will add an API route that will execute the getEvents query and return the results as JSON. You could add the route to the existing src/routes/index.js. However, as an application grows, it would be better to separate routes into modules that contain related resources.
Create a new folder under src/routes named api. Under src/routes/api, create a new file named index.js. Add the following code to this file.
"use strict";
const events = require( "./events" );
module.exports.register = async server => {
await events.register( server );
};
Create a new file under src/routes/api named events.js. Add the following code to this file.
"use strict";
module.exports.register = async server => {
server.route( {
method: "GET",
path: "/api/events",
config: {
handler: async request => {
try {
// get the sql client registered as a plugin
const db = request.server.plugins.sql.client;
// TODO: Get the current authenticate user's ID
const userId = "user1234";
// execute the query
const res = await db.events.getEvents( userId );
// return the recordset object
return res.recordset;
} catch ( err ) {
console.log( err );
}
}
}
} );
};
Now update src/routes/index.js to register the new api routes.
"use strict";
const api = require( "./api" );
module.exports.register = async server => {
// register api routes
await api.register( server );
server.route( {
method: "GET",
path: "/",
handler: async ( request, h ) => {
return "My first hapi server!";
}
} );
};
Whew! You’re almost there! Insert a couple of test records into your database.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[events]
( userId, title, description, startDate, startTime, endDate, endTime )
VALUES
( 'user1234', N'doctor appt', N'Stuff', '2019-10-03', '14:30', NULL, NULL )
, ( 'user1234', N'conference', N'', '2019-09-17', NULL, '2019-09-20', NULL )
Start the web server from the command/terminal window.
node .
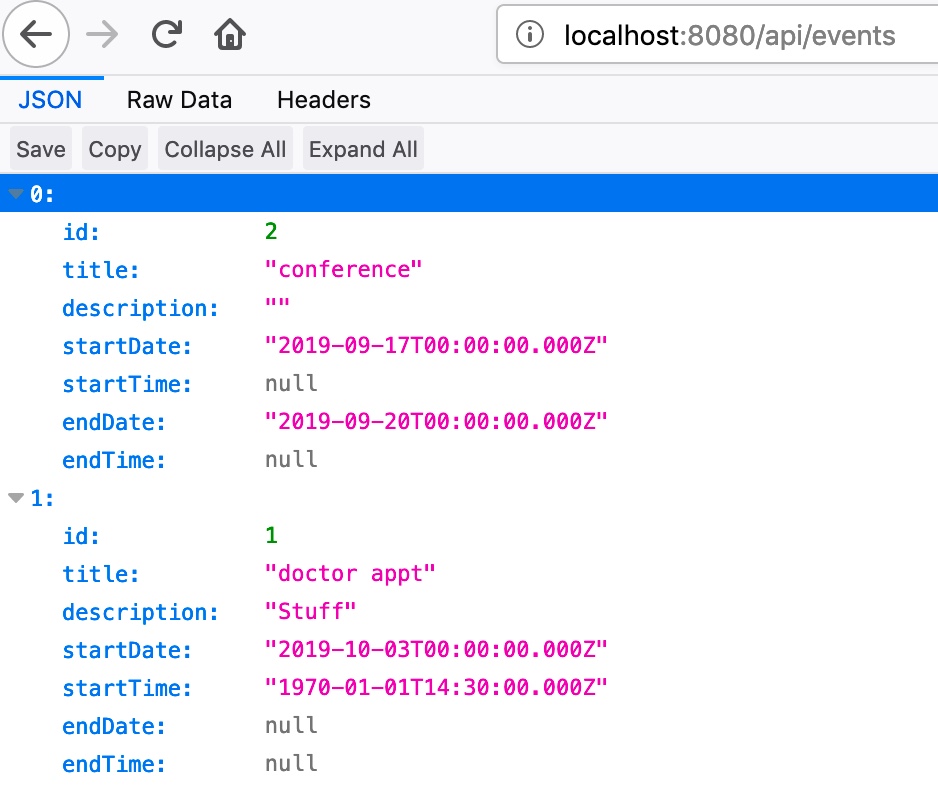
Now navigate your browser to http://localhost:8080/api/events. If everything is set up correctly, you should see a JavaScript array of the records you just inserted!
Add Authentication to Your Node.js Application
Let’s get some real users in the application! Manually building authentication and user profile management for any application is no trivial task. And, getting it wrong can have disastrous results. Okta to the rescue!
Before you begin, you’ll need a free Okta developer account. Install the Okta CLI and run okta register to sign up for a new account. If you already have an account, run okta login.
Then, run okta apps create. Select the default app name, or change it as you see fit.
Choose Web and press Enter.
Select Other.
Then, change the Redirect URI to http://localhost:8080/authorization-code/callback and accept the default Logout Redirect URI of http://localhost:8080.
What does the Okta CLI do?
The Okta CLI will create an OIDC Web App in your Okta Org. It will add the redirect URIs you specified and grant access to the Everyone group. You will see output like the following when it’s finished:
Okta application configuration has been written to: /path/to/app/.okta.env
Run cat .okta.env (or type .okta.env on Windows) to see the issuer and credentials for your app.
export OKTA_OAUTH2_ISSUER="https://dev-133337.okta.com/oauth2/default"
export OKTA_OAUTH2_CLIENT_ID="0oab8eb55Kb9jdMIr5d6"
export OKTA_OAUTH2_CLIENT_SECRET="NEVER-SHOW-SECRETS"
Your Okta domain is the first part of your issuer, before /oauth2/default.
NOTE: You can also use the Okta Admin Console to create your app. See Create a Web App for more information.
Copy your Okta values into the .env file to replace the {...} placeholders.
OKTA_ORG_URL=https://{yourOktaDomain}
OKTA_CLIENT_ID={yourClientId}
OKTA_CLIENT_SECRET={yourClientSecret}
Next, enable self-service registration. This will allow new users to create their own account. Run okta login to get the URL for your Okta org. Open the result in your favorite browser and log in to the Okta Admin Console.
- Click on the Directory menu and select Self-Service Registration.
- Click on the Enable Registration button.
- If you don’t see this button, click Edit and change Self-service registration to Enabled.
- Click the Save button at the bottom of the form.
Build a UI with Embedded JavaScript and Vue.js
In these next steps, you will add a frontend to your Node.js application using Embedded JavaScript (EJS) templates and Vue.js.
First, you will install a few dependencies needed to support authentication, rendering templates, and serving static files.
npm install bell@9 boom@7 ejs@2 hapi-auth-cookie@9 inert@5 vision@5
Register UI and Authentication Plugins
You will use bell to authenticate with Okta and hapi-auth-cookie to manage user sessions. Create a file under src/plugins named auth.js and add the following code.
"use strict";
const bell = require( "bell" );
const authCookie = require( "hapi-auth-cookie" );
const isSecure = process.env.NODE_ENV === "production";
module.exports.register = async server => {
// register plugins
const config = server.app.config;
await server.register( [ authCookie, bell ] );
// configure cookie authorization strategy
server.auth.strategy( "session", "cookie", {
password: config.cookiePwd,
redirectTo: "/authorization-code/callback", // If there is no session, redirect here
isSecure // Should be set to true (which is the default) in production
} );
// configure bell to use your Okta authorization server
server.auth.strategy( "okta", "bell", {
provider: "okta",
config: { uri: config.okta.url },
password: config.cookiePwd,
isSecure,
location: config.url,
clientId: config.okta.clientId,
clientSecret: config.okta.clientSecret
} );
};
Next, you will update src/plugins/index.js to register the auth.js module and add support for serving files related to the UI.
"use strict";
const ejs = require( "ejs" );
const inert = require( "inert" );
const { join } = require( "path" );
const vision = require( "vision" );
const auth = require( "./auth" );
const sql = require( "./sql" );
const isDev = process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production";
module.exports.register = async server => {
// register plugins
await server.register( [ inert, sql, vision ] );
// configure ejs view templates
const filePath = join( process.cwd(), "src" );
server.views( {
engines: { ejs },
relativeTo: filePath,
path: "views",
layout: true
} );
// register authentication plugins
await auth.register( server );
};
The inert plugin is used to serve static files and vision adds support for rendering server-side templates. Here ejs is configured as the template engine.
Add Server Views
Create a folder under src named views. Under src/views add a new file named layout.ejs and add the following code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<title><%= title %></title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/icon?family=Material+Icons" rel="stylesheet">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/index.css">
</head>
<body>
<% include partials/navigation %>
<%- content %>
<script src="/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Add a new file to src/views named index.ejs and add the following code.
<div class="container">
<% if ( isAuthenticated ) { %>
<div id="app"></div>
<% } else { %>
<h1 class="header"><%= title %></h1>
<p><%= message %></p>
<% } %>
</div>
Create a new folder under src/views named partials. Under src/views/partials add a new file named navigation.ejs and add the following code.
<nav>
<div class="nav-wrapper">
<ul class="left">
<% if ( isAuthenticated ) { %>
<li><a class="waves-effect waves-light btn" href="/logout">Logout</a></li>
<% } else { %>
<li><a class="waves-effect waves-light btn" href="/login">Login</a></li>
<% } %>
</ul>
</div>
</nav>
Update Routes to Support Views and Authentication
Under src/routes add a new file named auth.js. Add the following code to this file.
"use strict";
const boom = require( "boom" );
module.exports.register = async server => {
// login route
server.route( {
method: "GET",
path: "/login",
options: {
auth: "session",
handler: async request => {
return `Hello, ${ request.auth.credentials.profile.email }!`;
}
}
} );
// OIDC callback
server.route( {
method: "GET",
path: "/authorization-code/callback",
options: {
auth: "okta",
handler: ( request, h ) => {
if ( !request.auth.isAuthenticated ) {
throw boom.unauthorized( `Authentication failed: ${ request.auth.error.message }` );
}
request.cookieAuth.set( request.auth.credentials );
return h.redirect( "/" );
}
}
} );
// Logout
server.route( {
method: "GET",
path: "/logout",
options: {
auth: {
strategy: "session",
mode: "try"
},
handler: ( request, h ) => {
try {
if ( request.auth.isAuthenticated ) {
// const idToken = encodeURI( request.auth.credentials.token );
// clear the local session
request.cookieAuth.clear();
// redirect to the Okta logout to completely clear the session
// const oktaLogout = `${ process.env.OKTA_ORG_URL }/oauth2/default/v1/logout?id_token_hint=${ idToken }&post_logout_redirect_uri=${ process.env.HOST_URL }`;
// return h.redirect( oktaLogout );
}
return h.redirect( "/" );
} catch ( err ) {
request.log( [ "error", "logout" ], err );
}
}
}
} );
};
Now, edit src/routes/index.js to change the home page so it renders the new EJS view.
"use strict";
const api = require( "./api" );
const auth = require( "./auth" );
module.exports.register = async server => {
// register api routes
await api.register( server );
// register authentication routes
await auth.register( server );
// home page route
server.route( {
method: "GET",
path: "/",
config: {
auth: {
strategy: "session",
mode: "optional"
}
},
handler: async ( request, h ) => {
try {
const message = request.auth.isAuthenticated ? `Hello, ${ request.auth.credentials.profile.firstName }!` : "My first hapi server!";
return h.view( "index", {
title: "Home",
message,
isAuthenticated: request.auth.isAuthenticated
} );
} catch ( err ) {
server.log( [ "error", "home" ], err );
}
}
} );
// Serve static files in the /dist folder
server.route( {
method: "GET",
path: "/{param*}",
handler: {
directory: {
path: "dist"
}
}
} );
};
Update API Routes and Add SQL Queries
You need to update the application API to query the database based on the currently logged in user. At minimum, you also need routes to create, update, and delete events, along with their respective SQL queries.
Create a new file under src/data/events named addEvent.sql. Add the following SQL to this file.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[events]
(
[userId]
, [title]
, [description]
, [startDate]
, [startTime]
, [endDate]
, [endTime]
)
VALUES
(
@userId
, @title
, @description
, @startDate
, @startTime
, @endDate
, @endTime
);
SELECT SCOPE_IDENTITY() AS id;
Create a new file under src/data/events named updateEvent.sql. Add the following SQL to this file.
UPDATE [dbo].[events]
SET [title] = @title
, [description] = @description
, [startDate] = startDate
, [startTime] = @startTime
, [endDate] = @endDate
, [endTime] = @endTime
WHERE [id] = @id
AND [userId] = @userId;
SELECT [id]
, [title]
, [description]
, [startDate]
, [startTime]
, [endDate]
, [endTime]
FROM [dbo].[events]
WHERE [id] = @id
AND [userId] = @userId;
Create a new file under src/data/events named deleteEvent.sql. Add the following SQL to this file.
DELETE [dbo].[events]
WHERE [id] = @id
AND [userId] = @userId;
Update src/data/events/index.js to contain the following code.
"use strict";
const utils = require( "../utils" );
const register = async ( { sql, getConnection } ) => {
// read in all the .sql files for this folder
const sqlQueries = await utils.loadSqlQueries( "events" );
const getEvents = async userId => {
// get a connection to SQL Server
const cnx = await getConnection();
// create a new request
const request = await cnx.request();
// configure sql query parameters
request.input( "userId", sql.VarChar( 50 ), userId );
// return the executed query
return request.query( sqlQueries.getEvents );
};
const addEvent = async ( { userId, title, description, startDate, startTime, endDate, endTime } ) => {
const pool = await getConnection();
const request = await pool.request();
request.input( "userId", sql.VarChar( 50 ), userId );
request.input( "title", sql.NVarChar( 200 ), title );
request.input( "description", sql.NVarChar( 1000 ), description );
request.input( "startDate", sql.Date, startDate );
request.input( "startTime", sql.Time, startTime );
request.input( "endDate", sql.Date, endDate );
request.input( "endTime", sql.Time, endTime );
return request.query( sqlQueries.addEvent );
};
const updateEvent = async ( { id, userId, title, description, startDate, startTime, endDate, endTime } ) => {
const pool = await getConnection();
const request = await pool.request();
request.input( "id", sql.Int, id );
request.input( "userId", sql.VarChar( 50 ), userId );
request.input( "title", sql.NVarChar( 200 ), title );
request.input( "description", sql.NVarChar( 1000 ), description );
request.input( "startDate", sql.Date, startDate );
request.input( "startTime", sql.Time, startTime );
request.input( "endDate", sql.Date, endDate );
request.input( "endTime", sql.Time, endTime );
return request.query( sqlQueries.updateEvent );
};
const deleteEvent = async ( { id, userId } ) => {
const pool = await getConnection();
const request = await pool.request();
request.input( "id", sql.Int, id );
request.input( "userId", sql.VarChar( 50 ), userId );
return request.query( sqlQueries.deleteEvent );
};
return {
addEvent,
deleteEvent,
getEvents,
updateEvent
};
};
module.exports = { register };
Update src/routes/api/events.js to contain the following code.
"use strict";
const boom = require( "boom" );
module.exports.register = async server => {
server.route( {
method: "GET",
path: "/api/events",
config: {
auth: {
strategy: "session",
mode: "required"
},
handler: async request => {
try {
// get the sql client registered as a plugin
const db = request.server.plugins.sql.client;
// get the current authenticated user's id
const userId = request.auth.credentials.profile.id;
// execute the query
const res = await db.events.getEvents( userId );
// return the recordset object
return res.recordset;
} catch ( err ) {
server.log( [ "error", "api", "events" ], err );
return boom.boomify( err );
}
}
}
} );
server.route( {
method: "POST",
path: "/api/events",
config: {
auth: {
strategy: "session",
mode: "required"
},
handler: async request => {
try {
const db = request.server.plugins.sql.client;
const userId = request.auth.credentials.profile.id;
const { startDate, startTime, endDate, endTime, title, description } = request.payload;
const res = await db.events.addEvent( { userId, startDate, startTime, endDate, endTime, title, description } );
return res.recordset[ 0 ];
} catch ( err ) {
server.log( [ "error", "api", "events" ], err );
return boom.boomify( err );
}
}
}
} );
server.route( {
method: "DELETE",
path: "/api/events/{id}",
config: {
auth: {
strategy: "session",
mode: "required"
},
response: {
emptyStatusCode: 204
},
handler: async request => {
try {
const id = request.params.id;
const userId = request.auth.credentials.profile.id;
const db = request.server.plugins.sql.client;
const res = await db.events.deleteEvent( { id, userId } );
return res.rowsAffected[ 0 ] === 1 ? "" : boom.notFound();
} catch ( err ) {
server.log( [ "error", "api", "events" ], err );
return boom.boomify( err );
}
}
}
} );
};
Add Vue.js
First, install dependencies for Vue.js and other packages used for the UI.
npm install axios@0.21.1 luxon@1 materialize-css@1 moment@2 vue@2 vue-datetime@latest weekstart@1
Create a new folder at the root of the project named client. In this folder, add a new file named index.js. Add the following code to this file.
import Datetime from "vue-datetime";
import Vue from "vue";
import "materialize-css";
import "materialize-css/dist/css/materialize.min.css";
import "vue-datetime/dist/vue-datetime.css";
import App from "./App";
Vue.use( Datetime );
new Vue( { // eslint-disable-line no-new
el: "#app",
render: h => h( App )
} );
Add a new file to client named App.vue. Add the following code to this file.
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<div class="row" id="eventList">
<h2>Event List</h2>
<table v-if="hasEvents">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Start</th>
<th>End</th>
<th>Title</th>
<th>Description</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="event in events" :key="event.id">
<td>{{ event.startDate }} {{ event.startTime }}</td>
<td>{{ event.endDate }} {{ event.endTime }}</td>
<td>{{ event.title }}</td>
<td>{{ event.description }}</td>
<td>
<button id="eventDelete" @click="confirmDeleteEvent(event.id)" class="btn-small"><i class="material-icons right">delete</i>Delete</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p v-if="noEvents">No events yet!</p>
</div>
<div class="row" id="eventEdit">
<h2>Add an Event</h2>
<form class="col s12" @submit.prevent="addEvent">
<div class="row">
<div class="input-field col s6">
<span class="datetime-label">Start Date</span>
<datetime v-model="startDate" input-id="startDate" type="date" value-zone="local" input-class="validate"></datetime>
<!-- <label for="startDate" class="datetime-label">Start Date</label> -->
</div>
<div class="input-field col s6">
<span class="datetime-label">Time</span>
<datetime v-model="startTime" input-id="startTime" type="time" minute-step="5" use12-hour="true" value-zone="local" input-class="validate"></datetime>
<!-- <label for="startTime" class="datetime-label">Time</label> -->
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="input-field col s6">
<span class="datetime-label">End Date</span>
<datetime v-model="endDate" input-id="endDate" type="date" value-zone="local" input-class="validate"></datetime>
<!-- <label for="endDate">End Date</label> -->
</div>
<div class="input-field col s6">
<span class="datetime-label">Time</span>
<datetime v-model="endTime" input-id="endTime" type="time" minute-step="5" use12-hour="true" value-zone="local" input-class="validate"></datetime>
<!-- <input v-model="endTime" ref="endTime" placeholder="" id="endTime" type="text" class="validate"> -->
<!-- <label for="endTime">Time</label> -->
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="input-field col s12">
<input v-model="title" ref="title" placeholder="Appointment" id="title" type="text" class="validate">
<label for="title">Title</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="input-field col s12">
<input v-model="description" ref="description" placeholder="Description" id="description" type="text" class="validate">
<label for="description">Description</label>
</div>
</div>
<button id="eventEditSubmit" class="btn" type="submit"><i class="material-icons right">send</i>Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
<div id="deleteConfirm" ref="deleteConfirm" class="modal">
<div class="modal-content">
<h2>Confirm delete</h2>
<p>Delete {{ selectedEvent }}?</p>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button @click="deleteEvent(selectedEventId)" class="modal-close btn-flat">Ok</button>
<button class="modal-close btn-flat">Cancel</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
import * as M from "materialize-css";
import moment from "moment";
export default {
name: "app",
computed: {
hasEvents() {
return this.isLoading === false && this.events.length > 0;
},
noEvents() {
return this.isLoading === false && this.events.length === 0;
}
},
data() {
return {
title: "",
description: "",
events: [],
isLoading: true,
startDate: "",
startTime: "",
endDate: "",
endTime: "",
selectedEvent: "",
selectedEventId: 0
};
},
methods: {
addEvent() {
const event = {
startDate: this.startDate ? moment( this.startDate ).format( "YYYY-MM-DD" ) : null,
startTime: this.startTime ? moment( this.startTime ).format( "YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:00" ) : null,
endDate: this.endDate ? moment( this.endDate ).format( "YYYY-MM-DD" ) : null,
endTime: this.endTime ? moment( this.endTime ).format( "YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:00" ) : null,
title: this.title,
description: this.description
};
axios
.post( "/api/events", event )
.then( () => {
this.startDate = "";
this.startTime = "";
this.endDate = "";
this.endTime = "";
this.title = "";
this.description = "";
this.loadEvents();
} )
.catch( err => {
this.msg = err.message;
console.log( err );
} );
},
confirmDeleteEvent( id ) {
const event = this.events.find( e => e.id === id );
this.selectedEvent = `'${ event.title }' on ${ event.startDate }${ event.startTime ? ` at ${ event.startTime }` : "" }`;
this.selectedEventId = event.id;
const dc = this.$refs.deleteConfirm;
const modal = M.Modal.init( dc );
modal.open();
},
deleteEvent( id ) {
axios
.delete( `/api/events/${ id }` )
.then( this.loadEvents )
.catch( err => {
this.msg = err.message;
console.log( err );
this.loadEvents();
} );
},
formatDate( d ) {
return d ? moment.utc( d ).format( "MMM D, YYYY" ) : "";
},
formatTime( t ) {
return t ? moment( t ).format( "h:mm a" ) : "";
},
formatEvents( events ) {
return events.map( event => {
return {
id: event.id,
title: event.title,
description: event.description,
startDate: this.formatDate( event.startDate ),
startTime: this.formatTime( event.startTime ),
endDate: this.formatDate( event.endDate ),
endTime: this.formatTime( event.endTime )
};
} );
},
loadEvents() {
axios
.get( "/api/events" )
.then( res => {
this.isLoading = false;
this.events = this.formatEvents( res.data );
} )
.catch( err => {
this.msg = err.message;
console.log( err );
} );
}
},
mounted() {
return this.loadEvents();
}
};
</script>
<style lang="css">
#app h2 {
font-size: 2rem;
}
.datetime-label {
color: #9e9e9e;
font-size: .8rem;
}
</style>
Add a Build Process
It is necessary to create a build process that transforms and bundles the client UI into formats compatible with most browsers. For Node.js applications, these build steps are typically added to the package.json file under scripts.
First, install the packages you will need for building the client files.
npm install --save-dev nodemon@1 npm-run-all@4 parcel-bundler@1 @vue/component-compiler-utils@2 vue-template-compiler@2
Note: The
--save-devargument instructsnpmto install these as developer dependencies as opposed to dependencies required for production at runtime.
Now, modify package.json and change the scripts section to match the following.
"scripts": {
"build": "parcel build client/index.js",
"dev:start": "npm-run-all build start",
"dev": "nodemon --watch client --watch src -e js,ejs,sql,vue,css --exec npm run dev:start",
"start": "node .",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
You can run any script defined from the command/terminal using npm run [label] where label is any of the labels defined under scripts. For example, you can run just the build step using npm run build.
By the way, nodemon is a fantastic utility that watches for changes to files and automatically restarts the Node.js application. You can now start the new build process and launch the web application with one command.
npm run dev

I hope you have enjoyed learning how to use SQL Server with Node.js! You get the final source code for this project on GitHub, which also includes a few extras, such as examples of tests and a task to automate initializing the SQL database.
Learn More About Node.js and SQL
Want to learn more about Node.js? Check out some of these useful resources!
- Use TypeScript to Build a Node API with Express
- Modern Token Authentication in Node with Express
- Build a Basic CRUD App with Angular and Node
- Simple Node Authentication
- Build a CRUD App with ASP.NET Core and Angular
Follow us for more great content and updates from our team! You can find us on Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn. Questions? Hit us up in the comments below.
Okta Developer Blog Comment Policy
We welcome relevant and respectful comments. Off-topic comments may be removed.